
In the Environment Variables dialog choose the row Path and click on Edit …: In the System Properties dialog switch to the tab Advanced and click on Environment Variables … at the bottom: For example, from looking through the code and branch/tag names for a package you can sometimes figure out the earliest time a version might have been released, can you do this from pypi directly. This will open the System Properties dialog. To edit the Path environment variable press Win+R to start Run and in the field Open enter: sysdm.cpl and click on OK. If the Command Prompt responds with an error Python was probably not added to the Path environment variable.
The x stands for the revision level and could change as new releases come out. If the command python -version responds with the correct version everything is working now: Windows: Win+R > type powershell > Enter/OK MacOS: Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal There are different versions of Python, but the two most popular ones are Python 2.7.x and Python 3.7.x. In the Command Prompt enter python -version to check if the Python version you downloaded and installed was setup successfully. You can search for it in the Windows 11 start menu by typing Command Prompt and press Enter to open it: To check if your installation was successful open the Windows Command Prompt. When you finish the installation successfully, you can close the Python installer.
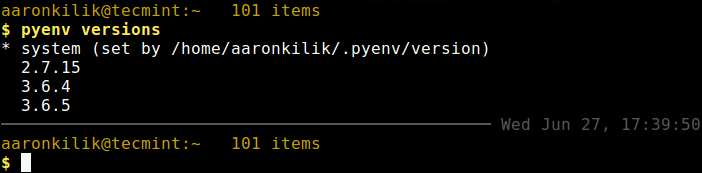
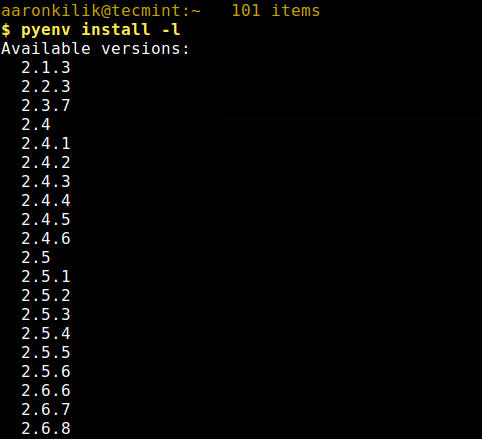
#See all python versions install
Then press Install Now to install Python together with additional Python tools such as pip on your computer: In the installer window, make sure to check Add Python 3.X to PATH this enables you to use the python, pip, etc.

When the download has finished, open your downloads folder and double click on the installer. To install the latest version of Python on Windows 11, head over to the Python download website and choose Windows Installer (64-bit) under the Stable Release section:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
